In a recent well written, compelling article published in Nature Communications, “Endothelial activation of caspase-9 promotes neurovascular injury in retinal vein occlusion,” Avrutsky et al show that caspase-9 inhibition is a promising treatment for retinal vein occlusion. Retinal vein occlusion models hypoxic-ischemic neurovascular damage and is the second leading cause of blindness in working-age adults. […]
Phoenix MICRON Research Blog
23.06
2020
Targeting VEGF164 in Müller cells may be useful to treat retinopathy of prematurity
In Nature’s Scientific Reports, Becker et al use the Phoenix MICRON® IV, OCT, and focal ERG to assess the therapeutic value of knocking down a splice variant of VEGF in Müller cells in a model of Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP). ROP is characterized by delayed vascularization of the retina after disrupted oxygen levels, followed by […]
20.05
2020
Imaging unanesthetized mice with the Phoenix MICRON® OCT provides consistent retinal degeneration measurements
In the recently published review, “Mouse Models of Inherited Retinal Degeneration with Photoreceptor Cell Loss,” researchers from The Jackson Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine and Mahidol University in Bangkok, Thailand performed an extensive literature search to find mouse models of single-gene mutations leading to photoreceptor loss and retinal degeneration. Using the Phoenix MICRON® III and […]
23.03
2020
The importance of ocular research on coronaviruses
As much of the world enacts restrictions to stem the spread of COVID-19, we thought we’d share something a little different than our usual highlight of Phoenix MICRON® research. Ivan Seah and Rupesh Agrawal recently published a review on the ocular implications of coronaviruses. Not much is known about ocular infection or transmission of the […]
18.02
2020
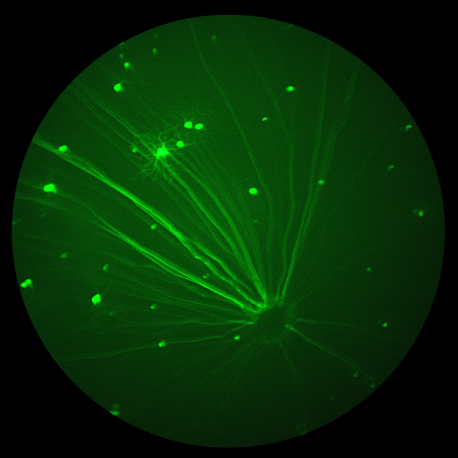
Retina as window to the brain: Stunning Phoenix MICRON® fluorescein angiography images of brain and retinal vasculature
Novel comparison of retina and brain vasculature leads to stunning Phoenix MICRON® images of fluorescent brain blood vessels The Phoenix MICRON® imaging platform produces stunning images of fluorescent retinal vasculature through fluorescein angiography but for the first time, researchers have also captured beautiful images of cortical brain vasculature. Hui et al, in their well-written and […]
30.01
2020
Measuring adeno-associated virus improvements with Phoenix MICRON® fluorescent imaging and Phoenix MICRON® Ganzfeld ERG
A team of researchers at the Indian Institutes of Technology have published three detailed articles examining how to improve adeno-associated viruses (AAV). Maurya, S, Mary, B, Jayandharan, GR et al -approach the improvement of the viruses in a stunningly detailed gene-to-cell-to-whole-mouse model, narrowing down a multitude of options and producing impressive fluorescent fundus images and […]