As Children’s Eye Health and Safety Month comes to a close, we want to shout out to all the researchers that are conducting groundbreaking pre-clinical studies, worldwide, to pioneer advancements in pediatric eye health. To all of you, thank you for your incredible work that is paving the way for better outcomes and brighter futures […]
16.08
2023
Small zebrafish are impressive, effective models for studying endotoxin induced uveitis
Researchers at Henan Province Eye Hospital in China have made great strides in studying endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) by creating a novel EIU model in zebrafish. Uveitis is an ocular inflammation and one of the main causes of visual impairment, accounting for 10-15% of global blindness. Mice have typically been the research animal of choice however […]
11.07
2023
Researchers find early signs of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the mouse retina and develop a non-invasive artificial intelligence-based system that could be used to diagnose the disease before the appearance of clinical symptoms
Progress in diagnosing and treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been accelerating over the last few years. Until now, AD has been difficult to diagnose. The disease can be present years before distinguishable symptoms manifest. Non-invasive diagnostic tests have been lacking, and diagnosis often relies on memory, cognitive, and behavioral tests. In 2011, Koronyo-Hamaoui M, Koronyo […]
27.01
2021
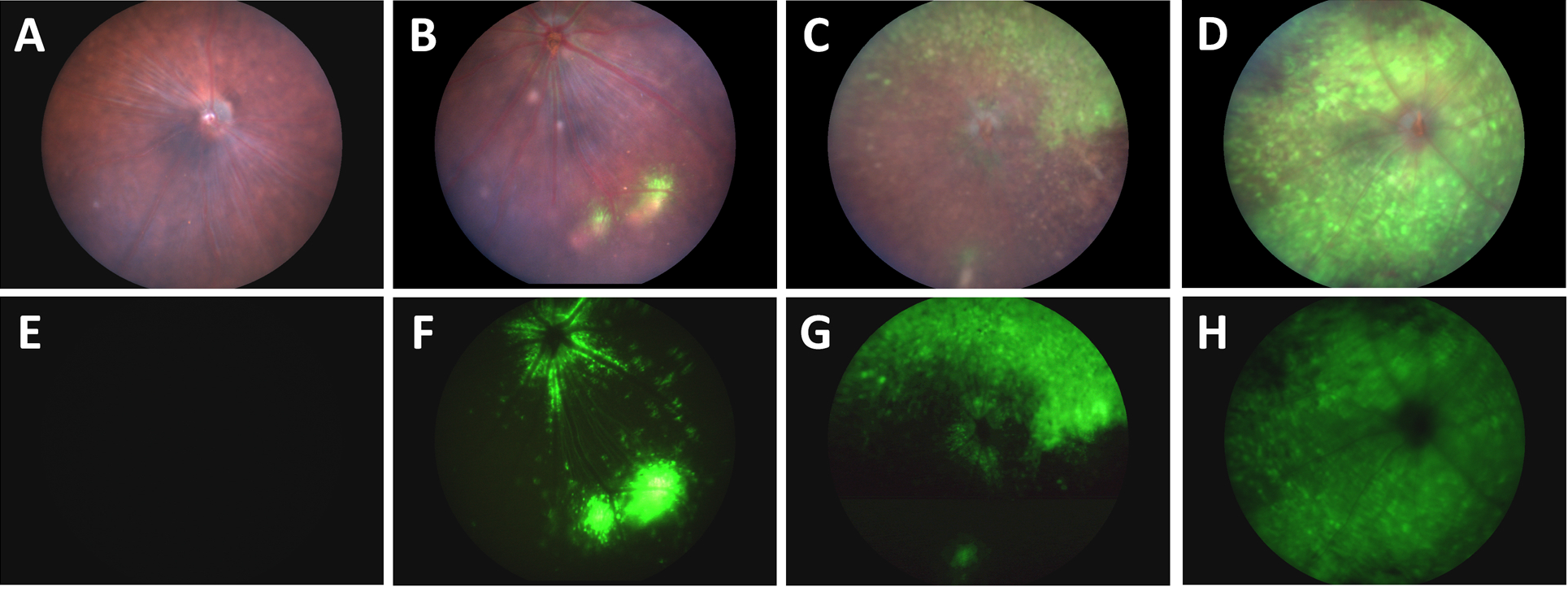
Stunning fundus images of GFP-positive cells demonstrate new intravitreal injection technique
In their article, “A Novel Method Combining Vitreous Aspiration and Intravitreal AAV2/8 Injection Results in Retina-Wide Transduction in Adult Mice,” Da Costa et al use the Phoenix MICRON® III imaging platform to take stunning images demonstrating the success of their novel intravitreal injection technique. Gene therapy is a promising treatment option of genetic retinopathies—adeno-associated viruses […]
18.11
2020
The Phoenix MICRON® IV system and OCT help evaluate promising compounds for treatment of age-related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration affects tens of millions of people worldwide, leading to vision impairment and blindness. Anti-VEGF treatment helps only 25-40% of patients, leaving others with no recourse to this progressive blinding disease. In their article, “Suppression of aberrant choroidal neovascularization through activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor,” Choudhary et al explore potential treatment using […]
27.03
2019
Phoenix MICRON® CNV System used to test a novel treatment for age-related macular degeneration
In their paper, “Suppression of Choroidal Neovascularization by AAV-Based Dual-Acting Antiangiogenic Gene Therapy,” Askou et al develop an adeno-associated virus (AAV) treatment for age-related macular degeneration. Beautiful fluorescent fundoscopy performed with the Phoenix MICRON® validated the success of the subretinal AAV injection, while precise choroidal neovascularization (CNV) induced by Phoenix laser burns confirmed that the […]