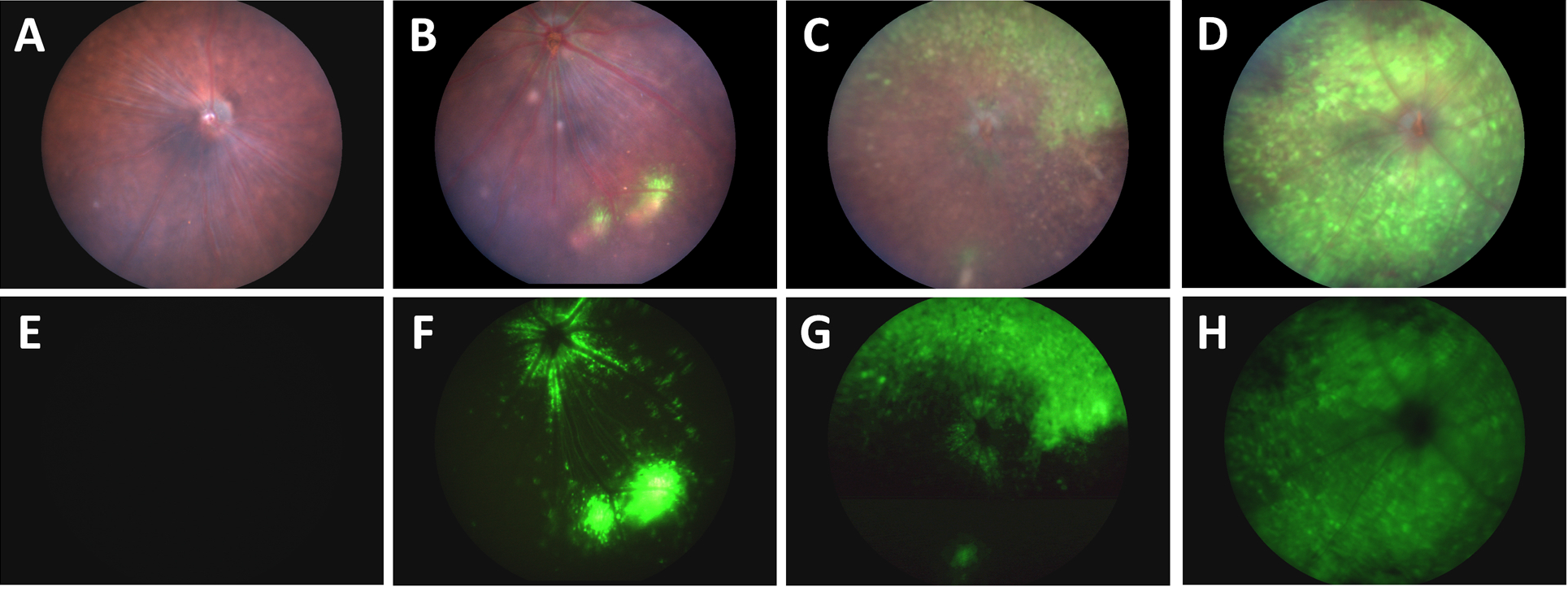
Hampel et al use the Phoenix MICRON® III imaging platform in an unusual manner in their paper “Relaxin 2 is functional at the ocular surface and promotes corneal wound healing by visualizing enucleated corneas.” The Phoenix MICRON® is designed to take crisp images and videos of the rodent retina, but this article demonstrates the other […]
Phoenix MICRON Research Blog
29.07
2021
Subretinal injection damage has implication for experimental control and treatment in rat model of retinopathy of prematurity
In their 2017 article, “Effect of subretinal injection on retinal structure and function in a rat oxygen-induced retinopathy model,” Becker et al used the Phoenix MICRON® IV fundus camera, Phoenix MICRON® OCT2 and corresponding layer analysis software Insight 2D, and the Phoenix MICRON® focal ERG to find that subretinal injection of saline or even introduction […]
24.06
2021
Promising treatment for retinal inflammation studied with the Phoenix MICRON® OCT and exclusive analysis software Insight 2D
In their paper, “Connexin43 Mimetic Peptide Improves Retinal Function and Reduces Inflammation in a Light-Damaged Albino Rat Model,” Guo et al promoted neuroretinal survival in a light damage paradigm by blocking the Connexin43 hemichannels. Using the Phoenix MICRON® OCT to examine the structure of the retina at precise retinal locations as shown by the bright […]
25.03
2021
Therapeutic target for retinal degeneration studied with the Phoenix MICRON® retinal structure and function tools
In their article, “Effect of MMP-9 gene knockout on retinal vascular form and function,” George et al study the effect of knocking out a matrix protein in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa using the Phoenix MICRON® platform including OCT, and Ganzfeld ERG. The combination of the Phoenix MICRON® fundus images, OCT revealing the layers, […]
25.02
2021
A better mouse model of retinal vein occlusion with the Phoenix MICRON® laser and OCT
Retinal vein occlusion is the second most common retinal vascular disorder leading to loss of vision in developed countries (after diabetic retinopathy). A lack of treatment options is partially caused by a lack of effective animal models; most rodent models do not show the essential symptom of cystoid edema and often heal quickly. In their […]
27.01
2021
Stunning fundus images of GFP-positive cells demonstrate new intravitreal injection technique
In their article, “A Novel Method Combining Vitreous Aspiration and Intravitreal AAV2/8 Injection Results in Retina-Wide Transduction in Adult Mice,” Da Costa et al use the Phoenix MICRON® III imaging platform to take stunning images demonstrating the success of their novel intravitreal injection technique. Gene therapy is a promising treatment option of genetic retinopathies—adeno-associated viruses […]