In the recently published review, “Mouse Models of Inherited Retinal Degeneration with Photoreceptor Cell Loss,” researchers from The Jackson Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine and Mahidol University in Bangkok, Thailand performed an extensive literature search to find mouse models of single-gene mutations leading to photoreceptor loss and retinal degeneration. Using the Phoenix MICRON® III and […]
Phoenix MICRON Research Blog
23.03
2020
The importance of ocular research on coronaviruses
As much of the world enacts restrictions to stem the spread of COVID-19, we thought we’d share something a little different than our usual highlight of Phoenix MICRON® research. Ivan Seah and Rupesh Agrawal recently published a review on the ocular implications of coronaviruses. Not much is known about ocular infection or transmission of the […]
18.02
2020
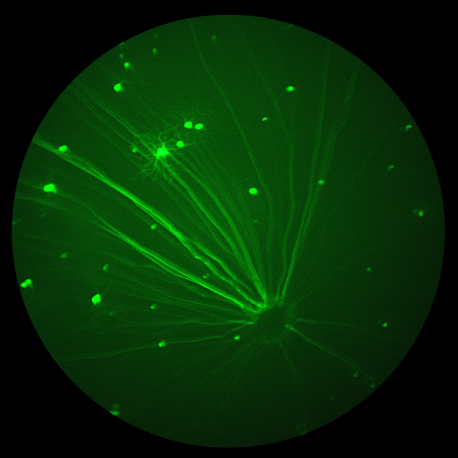
Retina as window to the brain: Stunning Phoenix MICRON® fluorescein angiography images of brain and retinal vasculature
Novel comparison of retina and brain vasculature leads to stunning Phoenix MICRON® images of fluorescent brain blood vessels The Phoenix MICRON® imaging platform produces stunning images of fluorescent retinal vasculature through fluorescein angiography but for the first time, researchers have also captured beautiful images of cortical brain vasculature. Hui et al, in their well-written and […]
30.01
2020
Measuring adeno-associated virus improvements with Phoenix MICRON® fluorescent imaging and Phoenix MICRON® Ganzfeld ERG
A team of researchers at the Indian Institutes of Technology have published three detailed articles examining how to improve adeno-associated viruses (AAV). Maurya, S, Mary, B, Jayandharan, GR et al -approach the improvement of the viruses in a stunningly detailed gene-to-cell-to-whole-mouse model, narrowing down a multitude of options and producing impressive fluorescent fundus images and […]
09.11
2019
Treating retinitis pigmentosa with cassia seed: Retinal layer analysis with the Phoenix MICRON OCT and Insight software
Retinitis pigmentosa is a genetic disorder that leads to severe vision impairment and blindness. The photoreceptors die off in a self-propelling cycle of rod and cone dysfunction, leading to glial activation and death, leading to more dysfunction. There are a few experimental treatments but no widespread effective treatment or cure. Cassia seed is used in […]
21.10
2019
Phoenix MICRON® FA reveals more leakage in iron-overload model of diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a crippling complication of diabetes that can lead to loss of vision, characterized by retinal inflammation, neurodegeneration, and disorganized microvascularization . Oxidative stress is crucial to the development of diabetic retinopathy. Iron is an essential micronutrient but, in excess, can become a highly damaging oxidative species. Excessive iron has been implicated in Parkinson’s […]