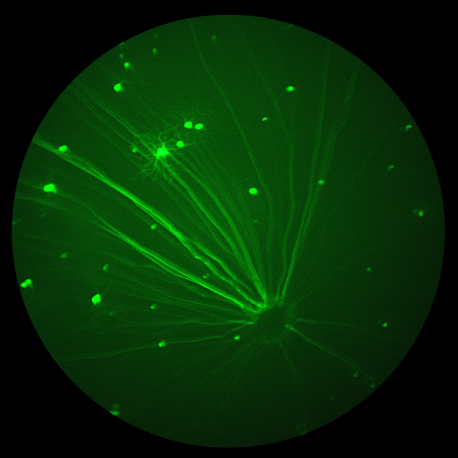
Microglia respond to neurological injury but the precise way they help to clear and remodel the injuries is not known. In their paper, “Optic nerve as a source of activated retinal microglia post-injury,” Heuss et al investigate a population of microglia-like cells that proliferate in the retina after an optic nerve injury. They identify GFPhi myeloid […]
21.07
2020
Caspase-9 inhibiting eyedrops rescue physiological and functional retinal vein occlusion damage shown with Phoenix MICRON®, OCT, and focal ERG
In a recent well written, compelling article published in Nature Communications, “Endothelial activation of caspase-9 promotes neurovascular injury in retinal vein occlusion,” Avrutsky et al show that caspase-9 inhibition is a promising treatment for retinal vein occlusion. Retinal vein occlusion models hypoxic-ischemic neurovascular damage and is the second leading cause of blindness in working-age adults. […]