Glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible vision loss, is characterized by progressive damage to retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and the optic nerve, often associated with increased intraocular pressure (IOP). While previous studies have implicated Tau protein expression and phosphorylation changes in other neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and glaucoma, the causative role […]
26.08
2020
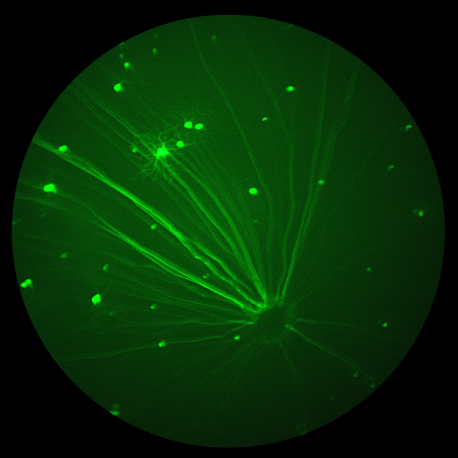
Phoenix MICRON® III shows microglia-like cells migrating from the optic nerve after injury
Microglia respond to neurological injury but the precise way they help to clear and remodel the injuries is not known. In their paper, “Optic nerve as a source of activated retinal microglia post-injury,” Heuss et al investigate a population of microglia-like cells that proliferate in the retina after an optic nerve injury. They identify GFPhi myeloid […]