Glaucoma, a leading cause of irreversible vision loss, is characterized by progressive damage to retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and the optic nerve, often associated with increased intraocular pressure (IOP). While previous studies have implicated Tau protein expression and phosphorylation changes in other neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and glaucoma, the causative role […]
17.01
2019
Characterizing a mutant rat strain with the Phoenix Micron OCT and Ganzfeld ERG
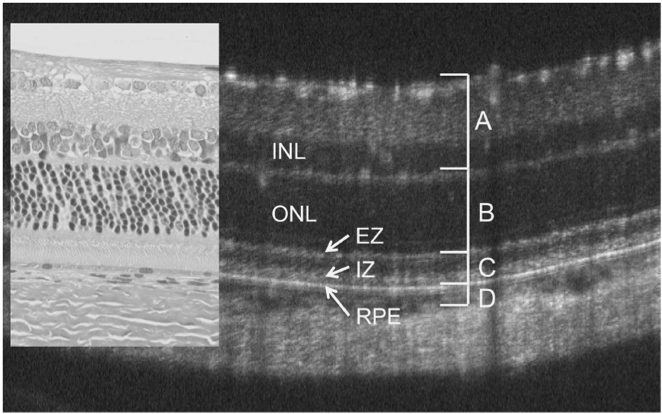
Monai et al characterized the longitudinal retinal degeneration of a rat model of retinitis pigmentosa using the Phoenix Micron OCT to examine retinal layers in live rats and the full field Ganzfeld ERG to test function. The rats have one of the mutations, P23H, that cause retinitis pigmentosa in humans, and are specifically a very […]